Timed perfusion protocols
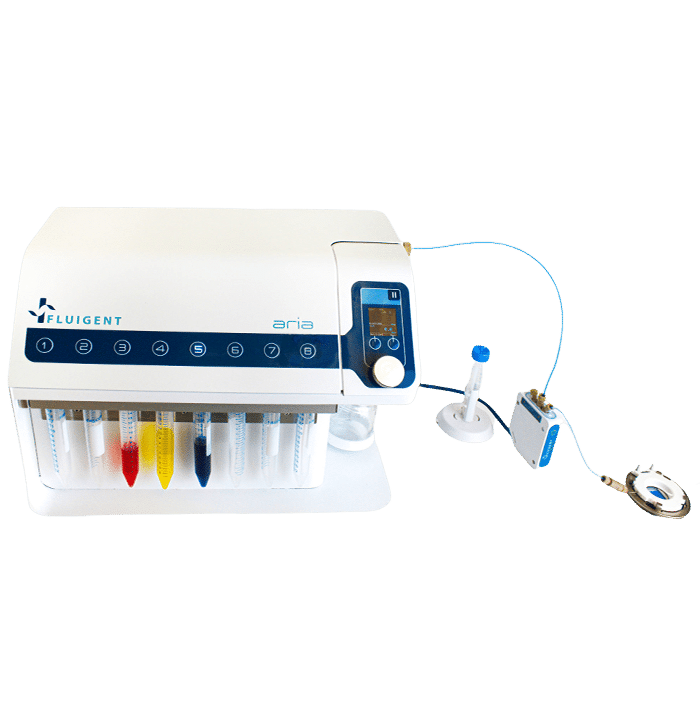
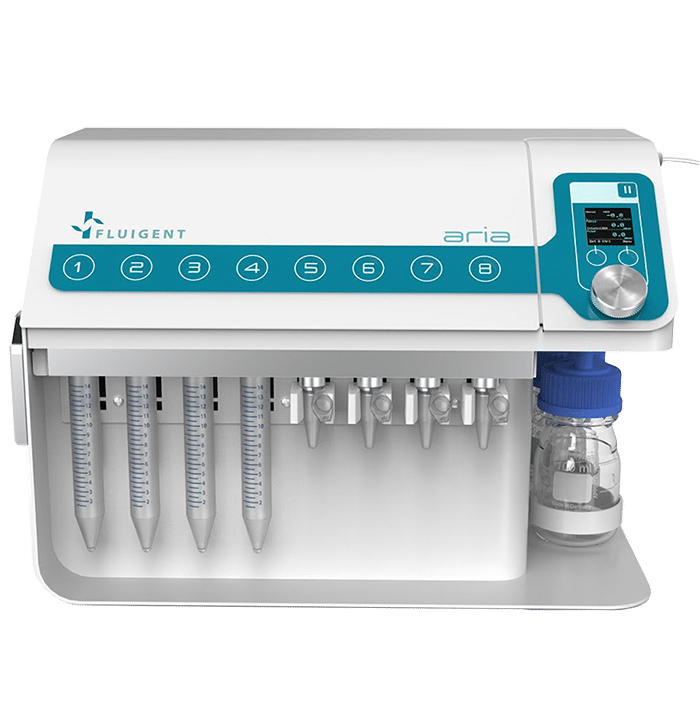
Aria, An Automated Perfusion System
[OAR]- Best Seller
Platform for Spatial Omics
Fluigent’s Aria, an all-inclusive and user-friendly automated perfusion system is tailored for spatial omics applications. It’s an ideal solution for automating Immunolabeling, FISH, and DNA-paint experiments, and it can easily adapt to other similar protocols requiring sequential controlled cellular perfusion or timed fluid delivery.
In workflows involving cellular/tissue perfusion and long-term imaging, maintaining controlled experimental conditions provides more consistent data. The Aria provides reproducible fluid volumes at precise times for cell and tissue culture and perfusion.
- Automation
- Biocompatible
Contamination-free
- Save time
Automated protocols
- Easy to use
All in one instrument and software
- Adaptable
Fits any experimental design
- Versatile
Can Communicate with most microscope software
Aria Application Examples
Our automated perfusion system can be used for a wide range of applications including ones that synchronize with microscopy.
Examples are as follows:
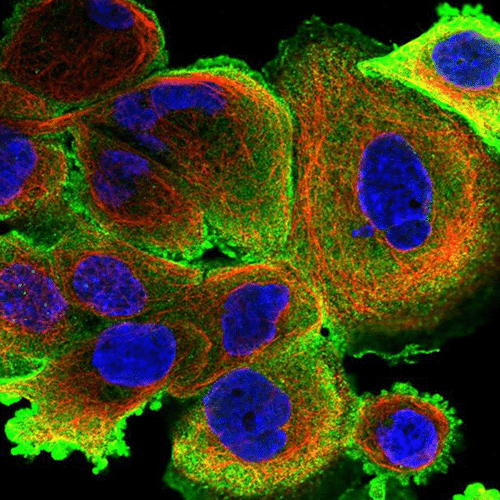
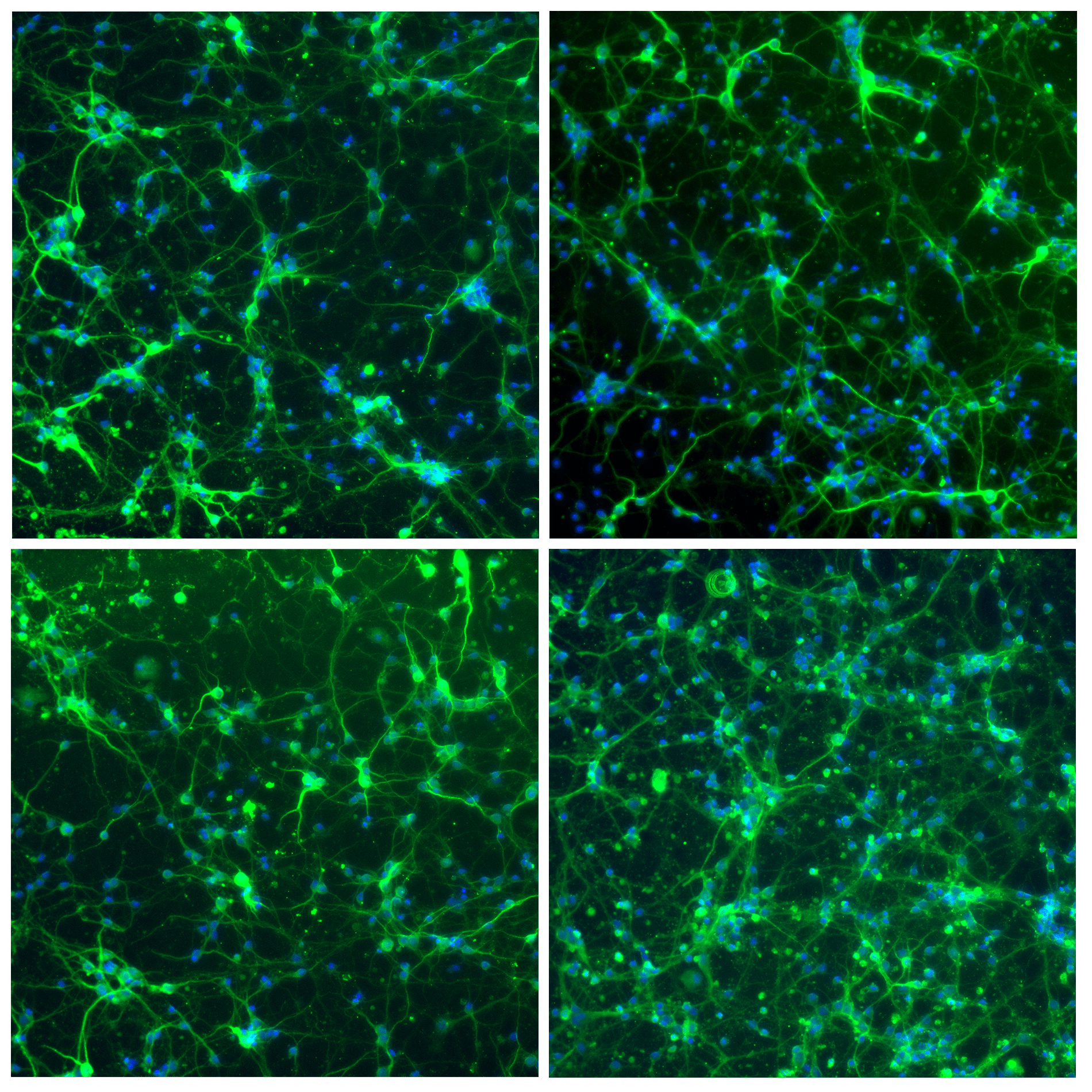
- Neuron cell immunolabeling in microfluidic chips: Aria facilitates parallel neuronal cell immunofluorescence in up to four microfluidic chips. By automating the cell immunolabeling process, users can significantly reduce the time and effort required to perform the experiment while ensuring consistently stained cells with minimal cell damage and no antibody residue.
- Calcium imaging in neuron cells: Using Aria allows full automation of calcium imaging in neurons, expediting numerous microfluidic experiments. This ensured stable recordings, enhancing reliability and reproducibility.
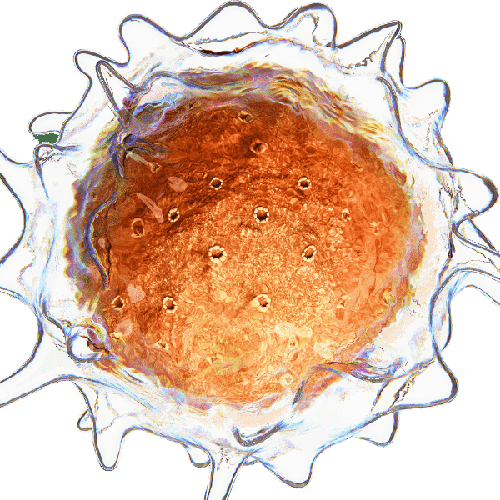
- Cancer cell capture and labeling: Aria can deliver up to 10 different solutions, automating the entire process of capturing and labelling MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. This includes surface treatment, injection of antibody-coated beads, cell suspension, and immunostaining. This streamlines cancer cell analysis, saving time, reducing reagent usage, and minimizing error margins.
Features of Aria
Deliver up to 10 solutions
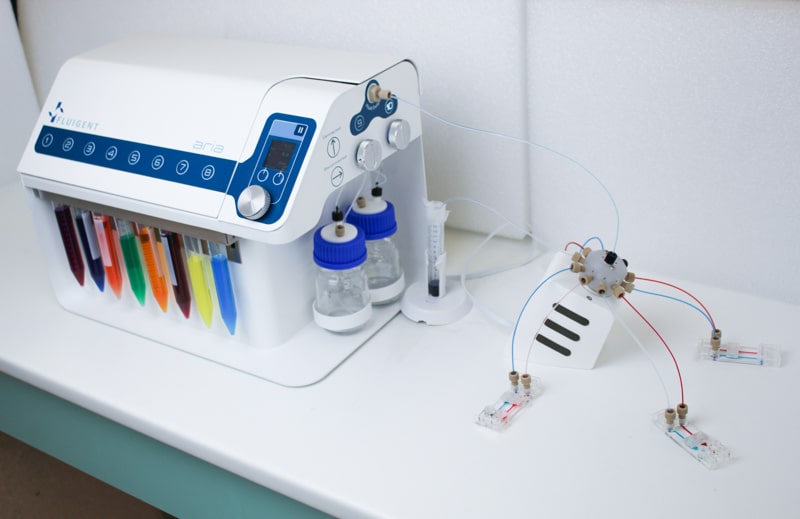
The Aria allows users to automate the delivery of up to 10 different solutions into a chamber or microfluidic chip by following user-defined protocols. It covers applications where the volumes injected range from 40 µL to hundreds of mL delivered over several days.
Intuitive software to automate any protocol
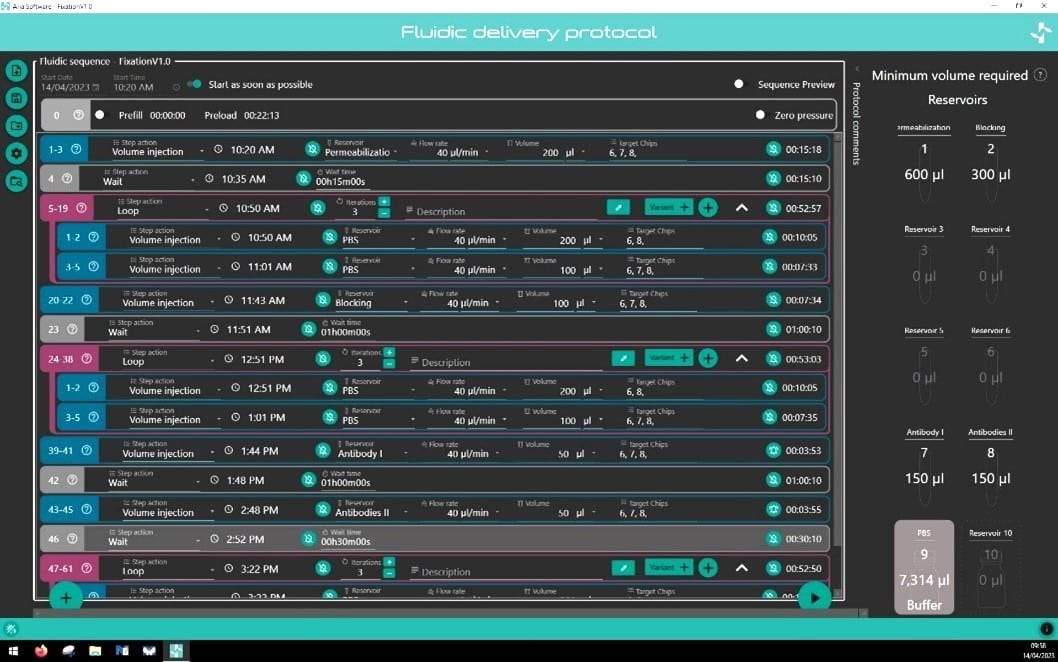
The perfusion system comes with intuitive software that helps facilitate complex protocol design in a few clicks. Incubation time, flow rate, and volume dispensed are all parameters that can be easily set by the operator for each step of the protocol. Protocols can be saved and recalled/edited for future use. The software notifies the user of the minimum volume required in each reservoir to run their protocol.
Preserve sample integrity
Our system generates minimal shear stress for cells and allows users to achieve liquid flow continuously. The sample is also maintained contamination-free, as no manual operations are done.
Ideal for imaging studies
Users can further automate imaging protocols by synchronizing it with various microscopes using TTL or TCP signaling. This is ideal for applications where long-duration or high-resolution imaging is needed. The Fluigent’s Aria software comes with a dark mode to work in an imaging room and is equipped with LEDs to facilitate use in dark areas.
Improve reproducibility
Fluigent’s Aria drastically reduces variability down to 0,5% between experiments compared to 5.1% intra-operator variability and 8.1% inter-operator variability using a pipette.
Publications
Media
Why use an automated perfusion system for spatial omics?
Applications like DNA hybridization, high-resolution spatial transcriptomics, DNA paint, FISH, immunolabeling, and tissue profiling require high-resolution microscopy as they target nanometric structures inside the cells. Many of these experiments require long imaging times which can now be automated.
WEBINAR: Automated IBEX multiplex immunohistochemistry with Aria
Are you considering automating your immunohistochemistry experiments with microfluidic-based technology? Meet Dr. Colin Chu from the UCL Institute of Ophthalmology, UK. He will guide you through the technique he helped develop with his team from the Germain Research Group at the US National Institutes of Health called “Iterative Bleaching Extends Multiplexity”, where they achieved the simultaneous labeling of up to 40 proteins within a single tissue section using Fluigent’s automated perfusion system, the Aria.
Have a live discussion with our experts and the option to discuss specific applications
WEBINAR: Enhancing Microfluidic Cell immunolabeling with Aria Technology
Discuss approaches to automating the cellular immunolabeling process using microfluidic devices, thereby increasing efficiency and reproducibility.
Agenda:
- Introduction to Fluigent’s expertise in the field of microfluidics and Organ-on-chip
- Aria: Fluigent’s automated sequential injection system
- Success story using Aria for neuron immunolabeling
- Have a live discussion with our experts and the option to discuss specific applications
WEBINAR REPLAY – Automating Cellular Studies with Aria
Watch the webinar by our team about Automating Cellular Studies with the Aria Automated Perfusion system.
The Aria system provides rapid experimental setup, ease of use, and can automate even multi-day protocols. It can interface with many microscopes to further simplify the process of reagent delivery and imaging. Aria is the best solution to automate your lab work. Highly flexible, it can adapt to any perfusion chamber and any protocol thanks to its intuitive software. Aria is also a tool for automating complex protocols for live-cell imaging (immunostaining, omics applications, radiometric imaging).
WEBINAR REPLAY – Automated fluid delivery for cell and tissue imaging
Want to gain time, precision and reproducibility for your immunofluorescence assay, or any other assay requiring injection of multiple solutions on your sample? Watch our webinar to learn how to interface a flow chamber (or microfluidic chip) to our automated fluid delivery device ARIA. This will allow you to deliver up to 10 different solutions in a sequential and autonomous manner. In addition, ARIA can be synchronized with any microscope to launch an image acquisition cycle and resume the perfusion protocol once the imaging cycle has been completed.
This all-in-one workflow facilitates alternation between cycles of injection/incubation time with reagents and image acquisition, a feature particularly well-adapted to complex cell and tissue imaging. Here we will present some example applications such as multiplexed tissue imaging, DNA-PAINT and seqFISH, as well as cell capture and staining.
WEBINAR REPLAY – How to turn your fluorescence microscope into a spatial omics platform
Current approaches in genomics, transcriptomics, and proteomics yield quantitative abundance analysis of biomolecules on an almost routine basis, with a critical impact in the life sciences.
However, coupling this high content to spatial information in a single-cell and tissue context is still a challenge, and this is where our efforts are presently focusing.
In this webinar, I will share my facility’s experience in building spatial omics platforms.
First, I will provide an overview and comparison of microscopy-based methods for spatial omics. Then, I will present details and resources on how to build such a platform.
Finally, I will show the existing tools available for image and data analysis associated with these methods.
It is my hope that our experience can serve others in the road ahead to help decide which technique is best for their applications and to assist in their implementation.
Reduce experimental error
Manually changing solutions under the microscope presents several challenges:
- Risk of displacing the dish and recorded positions of Regions of Interest (ROI)
- Potential loss of samples
- Increased risk of sample contamination
- Possibility of liquid spillage over the microscope
- Errors in the sequence of solutions due to the complexity of the process
Having an automated fluidic system reduces experiment duration, which can extend up to 4-5 days per experiment and requires constant scientist presence.
| Pipette | Aria | |
|---|---|---|
| Type of injections | Abrupt injection (up to 1mL in few seconds) Disparate injections Turbulent flow | Smooth & controlled injections Identical injections Laminar flow |
| Geometry at injection tip | Conic shape: important shear strain Unhomogeneous fluid velocity | Straight shape: No modification at the injection tip |

Seamless integration through our dedicated SDK
An SDK library allows users to customize the software to interface with external devices. This feature facilitates creation of exciting protocols with great potential, like the one featured in Nature Protocols. The authors developed an iterative immunolabeling and chemical bleaching method, called iterative bleaching extends multiplexity (IBEX), that enables multiplexed imaging (>65 parameters) in diverse tissues, including human organs.

“I got to test Aria automated sequential injection system in my research project in a collaboration with Fluigent. More precisely, Aria injection system helped me automatize the capture process and immunostaining of breast cancer cells under a very precise and controlled flow rate. The software interface is so user-friendly that I was being able to follow in real-time the progression of my experiment. The amazing part is that ARIA even calculated the total amount of time required for each step and helped me avoid the waiting time in front of my setup! It made my experiment go as smoothly as possible.”
Emile Lakis / Curie Institute, IPGG / Paris
Choose the perfusion system that best meets your needs
Single output version
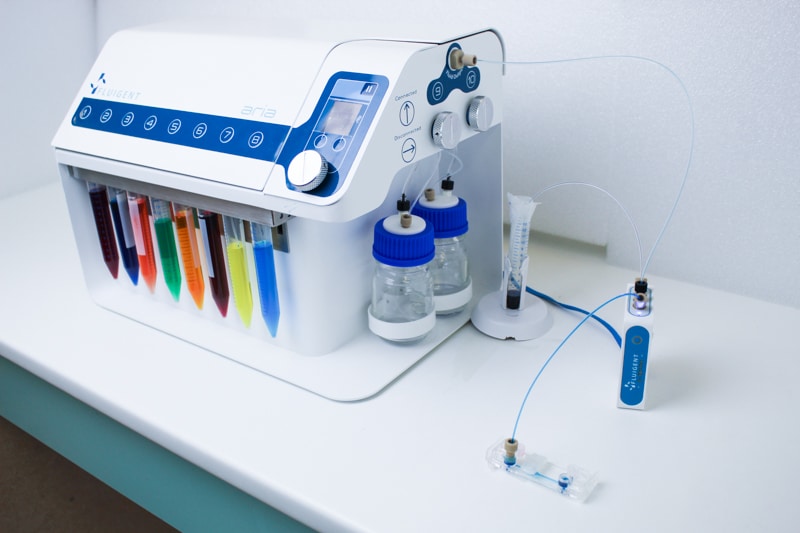
Perfect for high-quality multiplexed imaging experiments.
Aria is connected to a 2-switch to deliver up to 10 fluids into one sample.
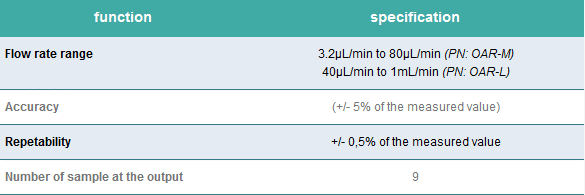
Serial output version

Automate staining or any routine protocols with multiple fluid delivery.
Aria is connected to an M-switch to deliver up to 10 fluids into 9 samples.
Perfect for high-quality multiplexed imaging experiments
Aria is the perfect compromise between manual pipetting and all-in-one systems that are dedicated to one specific application, integrating a microscope, specific chip type and a given set of solutions. Any protocol with multiple solution delivery can be automated, saving the scientist time and reducing variability between experiments compared to manual procedures. Discover our Automated Multiplexed Imaging Platform.

“Just wanted to say thanks again. We were able to run a 50 step Aria protocol on four separate occasions this weekend. Saved us more than a full day of work (~28 hours).”
M. Serrata / Wyss Institute / Boston, Massachusetts
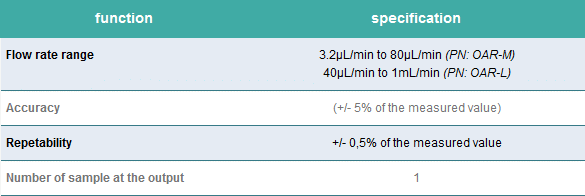
Specifications
PERFORMANCE
| Flow rate control | Over the range of 3,2 µL/min to 80 µL/min (Flow UNIT M) or 40 µL/min to 1 mL/min (Flow UNIT L) for water |
| Pressure control of flow rate | To a maximum of 2 bar |
| Valves | Ten position switching valve and two position switching valve |
| Fluid reservoirs | 15 mL standard, 2 mL available |
| Flushing solution reservoir | 100 mL |
| Tubing | FEP with OD of 1/16 inch and ID of 250 µm |
| Wetted surfaces | Polypropylene, FEP, Glass, PEEK, PCTFE, UHMW-PE, EPDM |
| Compressed air source | Requires non-corrosive, non-explosive, biocompatible compressed air (lab line, gas cylinder, compressor or Fluigent FLPG) |
| PC specifications | Windows 7 or higher |
HARDWARE SPECIFICATIONS
| Dimensions | 382 mm x 240 mm x 265 mm |
| Weight | 9 kg |
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
| Power supply voltage | 24V DC |
CHEMICAL COMPATIBILITY
| Gas compatibility | Dry, oil-free gas, air, any non-corrosive or non-explosive gas |
| Liquid compatibility | Aqueous solutions only |
Aria software
| Real-time control, protocol automation, data record and export. |
Aria SDK
| The SDK library collects the available software functions for users that wish to integrate our liquid handling functions into their own software for automated workflows, allowing them to have a single interface to actuate all components that are part of their fluorescence microscopy system (fluid management unit, imaging unit, heating devices, incubator, etc.). |
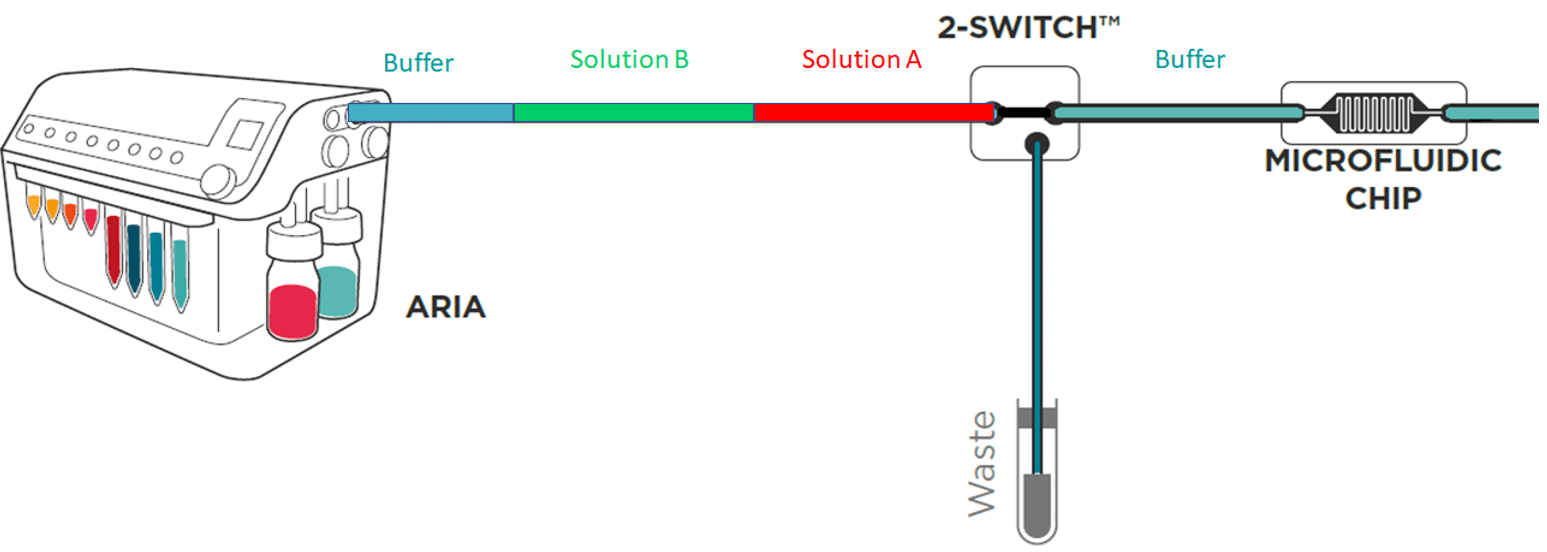
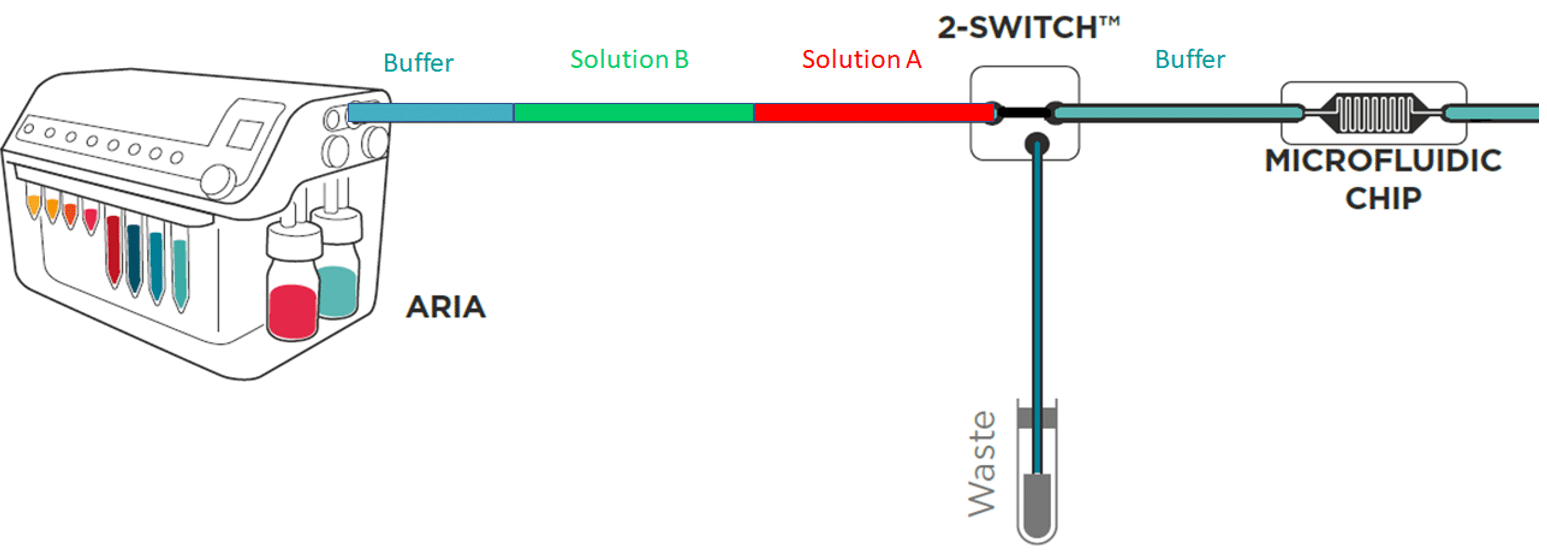
To save time and minimize reagents consumption, the system loads its internal and external tubing with the successive solutions to inject in the chip.
Working principle of the system
If the protocol commands to inject 40 µL of solution A, incubate for 1 hour, inject 50 µL of solution B, incubate for 1 hour then wash with buffer for 5 minutes and the total volume of tubing ( internal + external) is of 300 µL Aria will prefill tubing as follows:
As a consequence, calibration of the tubing length and related volume is necessary.
Here is a description of all the functions available to optimize protocol writing in Aria
Calibration of Aria
Calibration is automated and the software assists the user to determine the total volume of his step up (internal volume + L1+L2). Calibration values are recorded for future experiments.
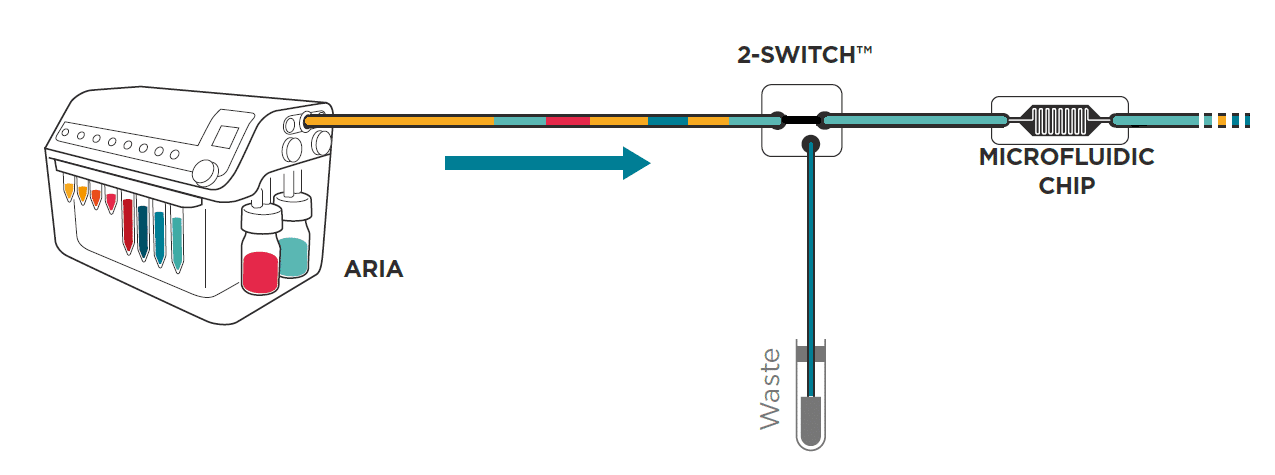
Prefill
Initially all tubing inside Aria is dry. The “Prefill” function is recommended as a first step to load all solutions inside the device without injecting air in the chip or chamber. This function can be deactivated if the user performed the loading manually. Fluigent strongly recommends using this function.
Perform perfusion & injection with Aria
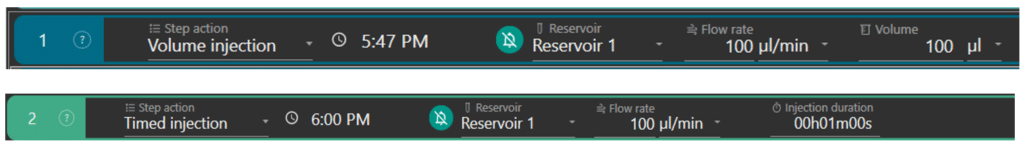
Perfusion can be set in terms of volume (ex: step 1) or duration (ex: step 2) of injection.
The user selects the reservoir of the solution to inject (ex: reservoir 1), sets the flow rate (ex: 100 µL/min) at which the solution will enter the flow cell and the volume (ex: 100 µL) or duration (ex: 1min) of injection. The flow rate range is from 40 µL/min to 1 mL/min. The software automatically calculates the time at which the solution should enter the flow cell.
Incubation / wait
Incubation time can be easily set by entering the duration of the incubation (ex: 1h30) in the ‘wait’ function.

The ‘wait for user’ function is a variation of the ‘wait’ function. It is particularly useful if the user must perform a manual operation like preparing cells before injection. The system waits until the user notifies that it can proceed to the next step. In absence of notification by the user, the system proceeds to the next steps after 12 h.

Clear tubing
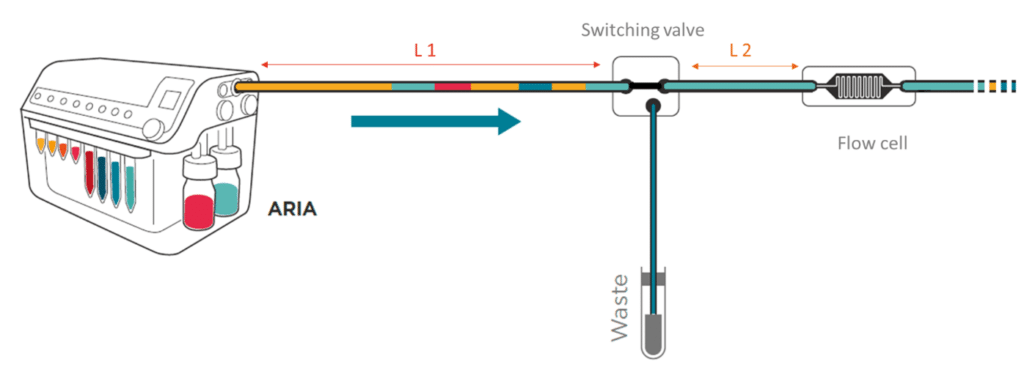
To prevent contamination between perfusion, the tubing can be cleared with a buffer using the ‘Flush tubing’ function. The user selects the reservoir containing the wash solution (ex: reservoir 10) and the flow rate at which the tubing is flushed (ex: 100 µL/min).

Aria pushes all the residual fluids contained in the L1 tubing to waste and fills the L1 with wash solution. The Buffer contained in L1 will also be directed to the waste. This operation does not involve flow to the chip as neither residual fluids nor buffer enter the chip. However, the residual fluid contained in L2 will not be cleared. For this reason, Fluigent recommends the user to keep L2 as short as possible.
External synchronization
Aria is equipped with TTL and TCP signalling and can send and receive both signals.
- Sending TTL or TCP
Each step is flanked by two bells () : at the front and back of the settings (see below for ‘volume injection step).

Click on each bell to begin activation. they get activated (). Aria will then send a TTL or TCP signal either when the step starts (example below) or ends or both.

Fluigent recommends using this function to synchronize perfusion and imaging.
- Receiving TTL or TCP
The ‘Wait for Signal’ function puts the Aria on hold. The Aria then waits for an external signal, either TTL on input port or TCP, to run the next steps. If the Aria does not receive signaling after 12 hours, it automatically proceeds with next steps.
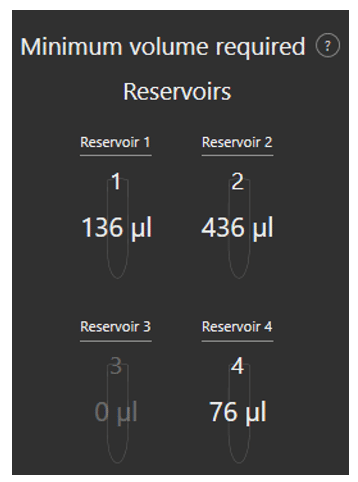
Minimum volume reservoir
Fluigent’s Aria is designed to minimize reagent consumption. An additional volume of liquid (36µL) is necessary to preload the system and to ensure that some residual liquid is still present in reservoir after perfusion to prevent delivery of air to the system.
As the user writes his protocol, the software calculates the minimum volume that should be placed in each reservoir to successfully run the protocol.
Write, load, save sequence
To design a new sequence, click on “Create new sequence”.
Before running a sequence, the software will automatically ask the user to save it.
All saved sequences are accessible and can be loaded by clicking on “Load sequence”.
Recorded data
For each experiment, the system automatically records and saves the flow rate, pressure, the reservoir from which the solution is withdrawn if solution is delivered to the chip or waste. All data is accessible by clicking on “open logs folder”
Expertise & resources
-
Microfluidic Application Notes Automating calcium imaging in neural cells with Fluigent’s Aria Read more
-
Microfluidic Application Notes Automating Neuronal Cell Immunofluorescence in Microfluidic Chips Read more
-
Fluigent products manual Aria SDK User Manual Download
-
Microfluidics Case Studies University of Rochester: A tissue chip platform for real-time sensing of secreted inflammatory markers using ARIA Read more
-
Fluigent Products Datasheets Aria Technical Specifications Download
-
Fluigent products manual Aria User Manual Download
-
Microfluidic Application Notes Cancer Cell Analysis Made Easy with Aria: cell Capture and Labeling Read more
-
Fluigent Products Datasheets Aria datasheet Download
-
Expert Reviews: Basics of Microfluidics Passive and active mechanical stimulation in microfluidic systems Read more