Microfluidic Markets & Applications
Learn the main microfluidic markets - from life sciences to the food industry- and why the related applications benefit from this technology.
Indeed many applications require the use of fluids driven at flow rates from nanoliters to milliliters per minute. At such low flows, the success of these applications strongly depends on the level of control and automation of the fluidic operations. Discover microfluidic applications requiring flow control systems that are adapted for ensuring their success.
What are the main advantages of microfluidics?
Microfluidics refers to the scientific field dedicated to managing and directing fluids, typically within the microliter (10-6) to picoliter (10-12) range, through intricate networks of channels ranging in size from tens to hundreds of micrometers. The discipline emerged in the early 1990s and has experienced explosive growth since then, becoming an indispensable tool in life science research and broader biotechnology applications.
Microfluidics holds many significant advantages that make it an attractive option for microfluidic markets. Its ability to operate at such small volumes can significantly reduce the consumption of reagents and samples, while also shortening experiment times and cutting overall costs for microfluidic applications.
What are the different microfluidic technologies existing?
Nowadays, three types of microfluidic pumps exist.
Peristaltic pumps
These pumps use a series of rollers or squeezing elements to compress a flexible tubing, creating a pulsatile flow into the microfluidic device.
Syringe pumps
These pumps use a syringe driven by a motor or a manual control to deliver continuous fluid flow into the microfluidic device.
Pressure controllers
They use compressed air or gas to generate targeted pressure and drive the fluid flow in the microfluidic device.
Each of these microfluidic pumps has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of the pump depends on the specific requirements of the application and microfluidic markets, such as flow rate, accuracy, precision, compatibility, and ease of use.
The main advantage of pressure controllers are their unmatched performance in terms of stability, accuracy and response time.
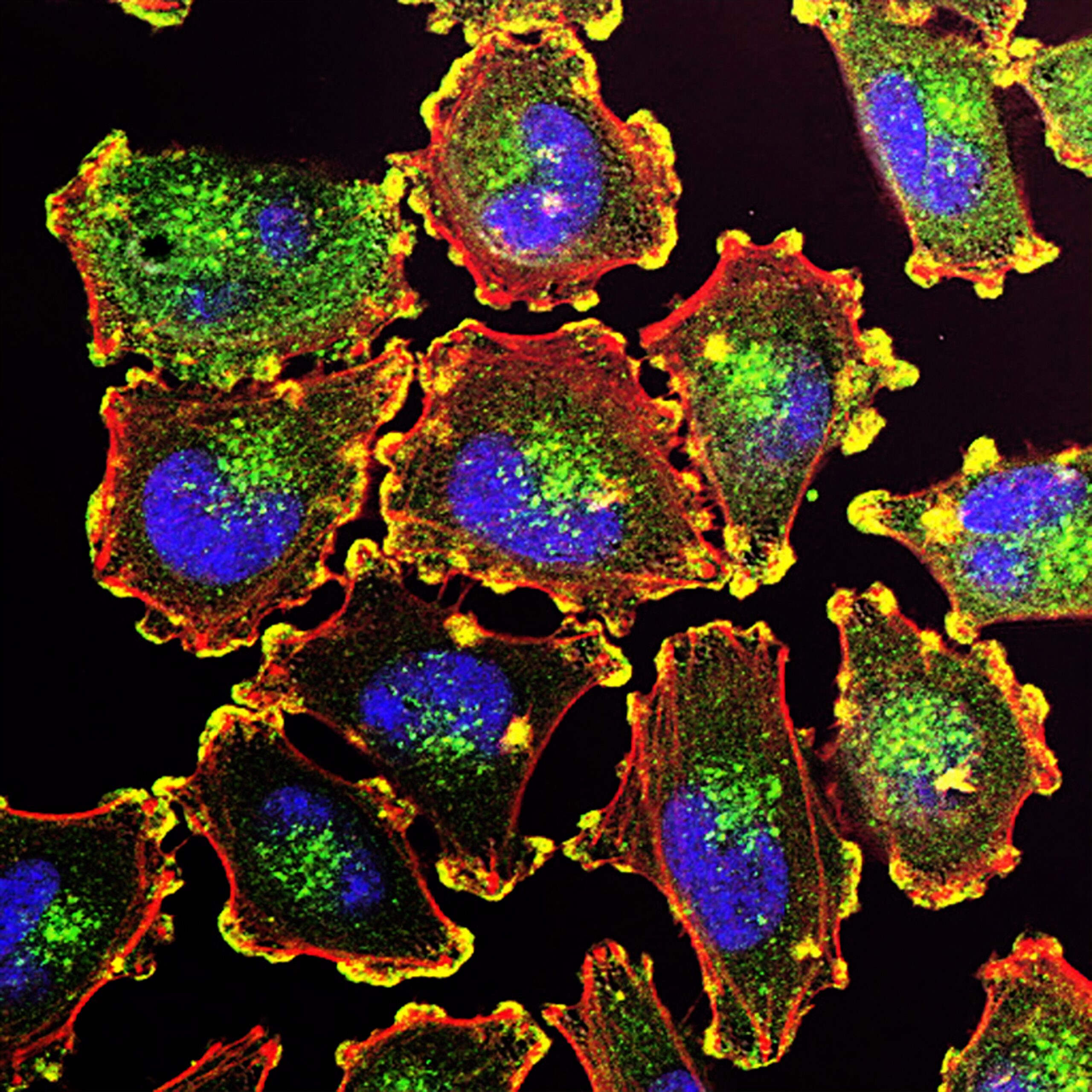
Life Science
Microfluidics is the technology of choice for many applications in the life sciences as it provides the ability to control cellular microenvironments with high spatiotemporal precision and presents cells with mechanical and biochemical signals in a more physiologically relevant context. Microfluidic markets & applications include super-resolution microscopy, (single) cell analysis, cell culture under perfusion or organs on a chip, molecular diagnostics, and more.
Pharmaceutics
Microfluidic technologies are expected to play an important part in future nanomedicine manufacturing and administration of therapeutic products and diagnostics as it meets the demand for high-quality and meticulously regulated medical products. Discover the main microfluidic markets in pharmaceutics, including drug development, drug screening, drug encapsulation and more below.


Food Industry
The rapidly growing global population demands more advanced technologies in food processing to produce more and safer food products. Microfluidic droplet generation systems are currently used for food processing, emulsification, and food safety measurements2. Discover the microfluidic markets in the food industry.
Cosmetics
The highly uniform and large droplets produced during a microfluidic emulsion can sometimes provide a sensual component to existing cosmetics.. In the case of preparing a monodisperse emulsion with a diameter of 1 mm, giant droplets can be visually pleasing3. From the perspective of performance and applicability, technological advances in engineering emulsion interfaces are strongly required. Discover the microfluidic markets for cosmetics.
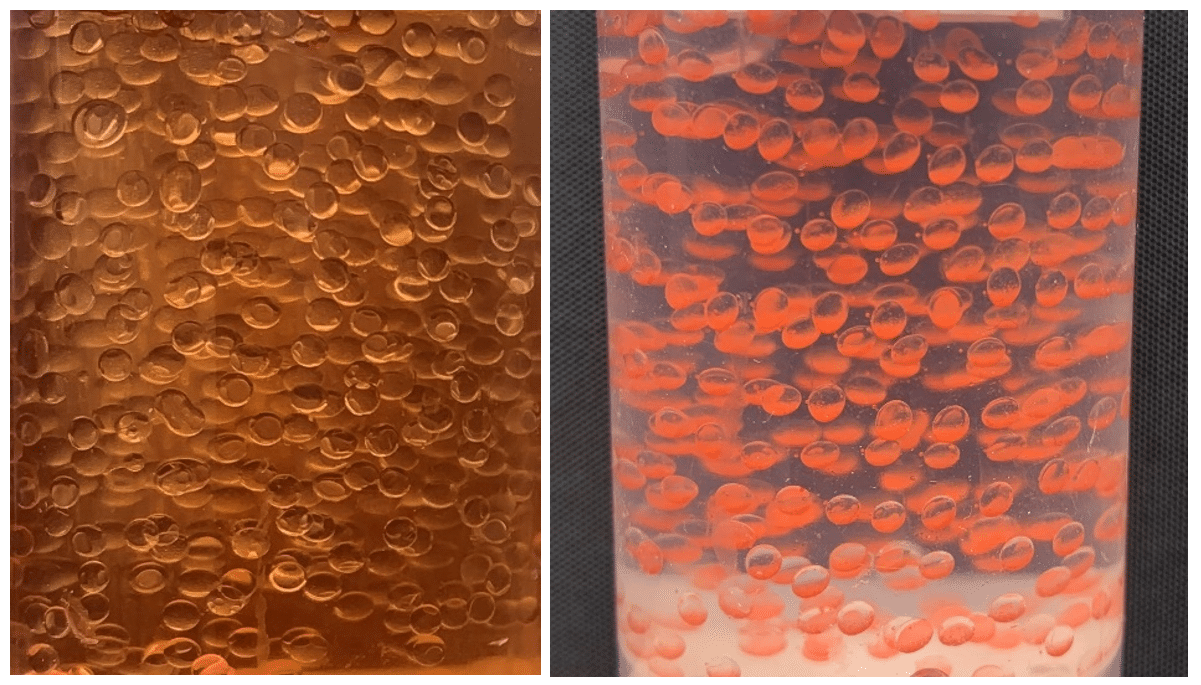

Water Analysis
Microfluidic devices provide a way to perform analyses at remote locations, enabling in situ measurement at the point of sampling. Reduced analysis times, sensitivity improvements, selectivity enhancement, and high repeatability are advantages of microfluidic devices when integrated into miniaturized chemical systems. Discover the microfluidic markets for water analysis.
Fluigent helps researchers and industry partners by providing best-in-class research instruments as well as industrial products and systems combined with strong expertise in fluid management.

Research Solutions
Our innovative, pressure-based microfluidic controllers are compatible with lab-on-a-chip devices and a wide variety of microfluidic technologies that will allow you to focus on the science for your microfluidic applications, not on the setup.
Resources & Expertises
- White Papers
An exploration of Microfluidic technology and fluid handling
Read more - Advantages of pressure-based microfluidics
Microfluidic pressure control for organ-on-a-chip applications: A comprehensive guide
Read more - White Papers
Microfluidic white paper – A review of Organ on Chip Technology
Read more - White Papers
Droplet-based Microfluidics
Read more - White Papers
Double emulsion for the generation of microcapsules – a Review
Read more - What is microfluidics?
What is the history of microfluidics?
Read more
References
1. Microfluidics Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Technology (Medical, Non-medical), By Application (Lab-on-a-chip, Organs-on-chips), By Material (Polymer, Silicon, Glass, PDMS), By Region, And Segment Forecasts, 2021 – 2028. https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/microfluidics-market (2019).
2. He, S., Joseph, N., Feng, S., Jellicoe, M. & Raston, C. L. Application of microfluidic technology in food processing. Food and Function vol. 11 5726–5737 Preprint at https://doi.org/10.1039/d0fo01278e (2020).
3. Are ‘microfluidics’ the next big beauty trend? Fashion Network (2017).
4. Park, D., Kim, H. & Kim, J. W. Microfluidic production of monodisperse emulsions for cosmetics. Biomicrofluidics vol. 15 Preprint at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0057733 (2021).