什么是组学?
“组学”是指专注于对细胞、组织或生物体内的生物大分子进行全方位分析的学科。 这些学科需要大规模分析各种生物组分(通常在分子水平),以获得对生物系统的全面了解。这种全方位分析需要使用特定的工具,以便通过生物信息学方法进行生物实验和数据分析。
下面是一些主要的组学学科:
- 基因组学:研究生物体的完整DNA组(基因组),以了解其结构、功能、变异以及基因之间的相互作用。
- 转录组学:研究细胞内的RNA分子,包括其类型、丰度和基因表达模式的变化。
- 蛋白质组学:研究细胞内的整个蛋白质组,分析其功能、结构、修饰、相互作用和丰度。
- 代谢组学:分析参与细胞代谢的完整小分子或代谢物组,深入了解代谢途径和生理变化。
- 表观基因组学:探索DNA序列之外的因素(如DNA甲基化和组蛋白修饰)引起的基因表达修饰和改变。
- 宏基因组学:专注于研究直接从环境样本中回收的遗传物质,深入了解微生物群落及其遗传多样性。
组学分析方法将从根本上改变生命科学领域的研究。这些方法能够评估单个细胞的基因组、转录组或蛋白质组,而不是评估细胞群内的平均状态,这标志着癌症生物学、神经科学、神经干细胞治疗等各个领域的重大飞跃。
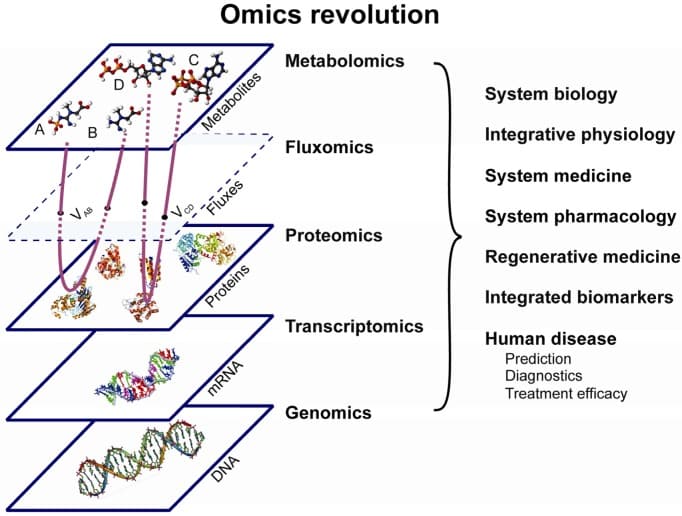
图1:“组学革命”–一种综合性的“组学”方法,结合了基因组学、转录组学、蛋白质组学、代谢组学和代谢流组学,可促进系统科学以及人类疾病的诊断和治疗的进步(1)。
组学学科领域使用的主要技术
这些组学学科推动了先进技术和高通量技术的发展,以生成大规模数据集。通过整合和分析这些数据集,研究人员可以了解复杂的生物过程和疾病机制,识别生物标志物,并为个性化医疗和靶向治疗创造条件。
组学技术得到了广泛使用,并且因所探索的特定组学领域而异。
- PCR(聚合酶链反应):用于基因组学,可成倍增加特定的DNA序列,从而对其进行分析和识别。
- 下一代测序(NGS):用于基因组学和转录组学,可对DNA和RNA进行测序,从而能够对基因组、基因表达、突变和变异进行大规模分析。
- 质谱(MS):用于蛋白质组学和代谢组学,可识别和量化样本中的蛋白质或代谢物,从而深入了解其结构、修饰、相互作用和浓度。
- 成像技术:应用于各个领域,用于可视化细胞或组织内的分子结构或分布,例如荧光显微镜、电子显微镜和成像质谱。
- 微阵列:用于基因组学和转录组学,可同时分析数千个基因或RNA的表达水平,从而实现基因表达模式的高通量筛选和比较。
- 色谱分析:用于代谢组学,可根据其化学性质分离和分析复杂的代谢物混合物,有助于其识别和定量分析。
- 生物信息学工具:对于处理、分析和解释组学技术生成的大量数据至关重要,涉及计算分析、统计建模和数据整合。
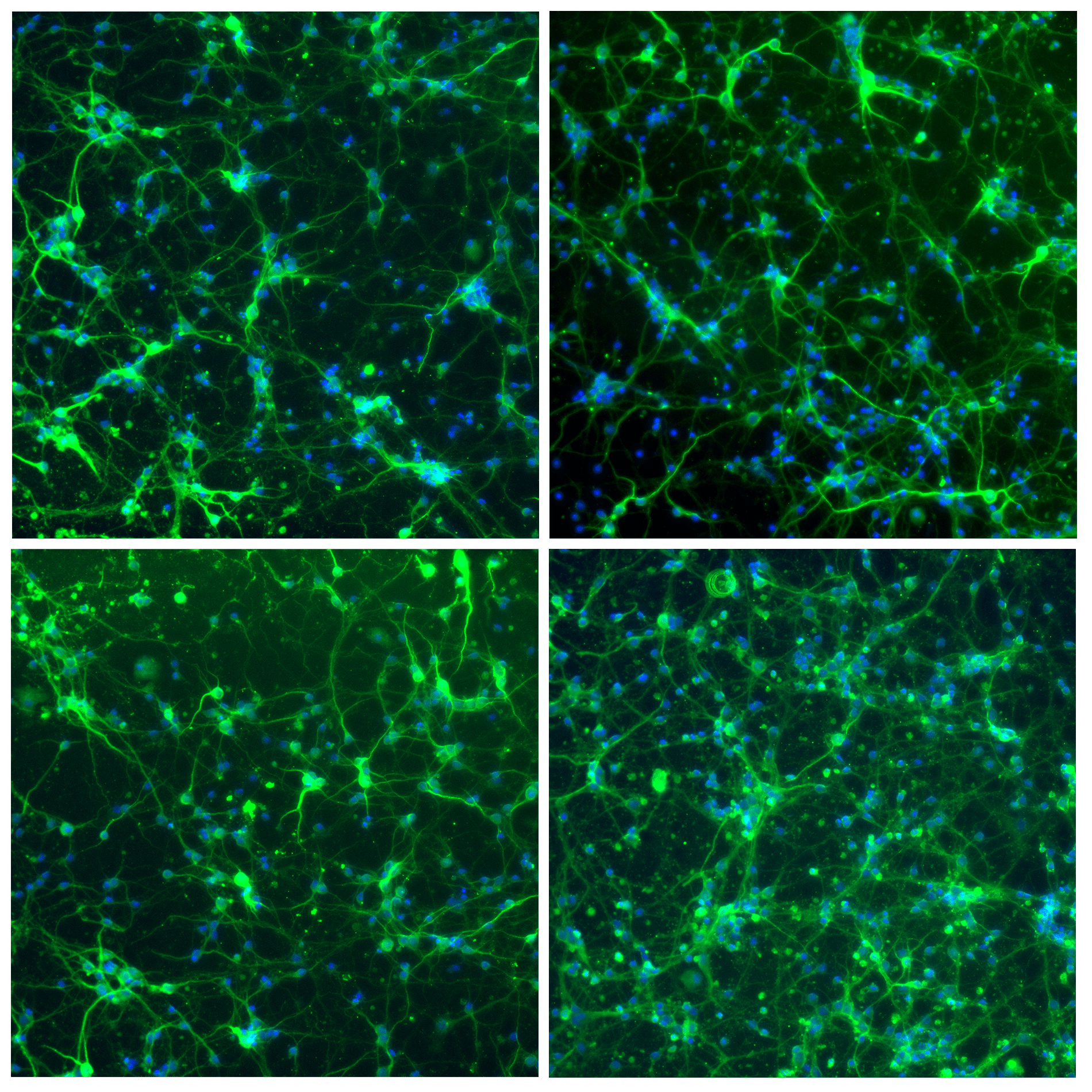
图2:微管相关蛋白2(绿色)和细胞核(蓝色)染色的神经元细胞免疫荧光。图像是在Nikon共焦显微镜上以10倍放大倍率拍摄的。
这些技术不断发展并与先进技术融合,有助于全面了解生物系统并推动生命科学领域的创新。
精确的流体处理和Fluigent对组学领域的贡献
组学领域的革命很大程度上归功于基于微流控的技术,这些技术通常需要将细胞分离成液滴、微通道或微孔,然后再进行首选的组学分析。
精确的流体处理是涉及DNA、RNA、蛋白质和代谢物的各种分析过程的基础。其对于样本制备等步骤至关重要,因为这些步骤需要准确移液、稀释和混合样本。如果将自动化和精确的流体处理相结合,则有利于实现基因组学、转录组学和蛋白质组学所使用的高通量筛选,从而能够有效地处理大量样本。
总体而言,确保样本制备、分离和分析的准确性和可重现性对于生成可靠的数据至关重要,这对在分子水平上理解生物系统做出了重大贡献。
在Fluigent,我们的核心使命是通过提供一系列致力于促进该领域进步的产品,推动科学前沿的发展,尤其是在充满活力的组学技术领域。
References
- Nielsen J, Oliver S. The next wave in metabolome analysis. Trends Biotechnol. 2005;23:544-6. Medline:16154652 doi:10.1016/j. tibtech.2005.08.005