Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR)
The science of microfluidic liquid handling for droplet digital PCR (ddPCR)
- Higher accuracy
- Higher sensitivity
- Absolute quantitation
What is digital PCR (dPCR)?
During the last decade digital-PCR (dPCR) has become one of the most prominent assays for analytical methods. dPCR carries out a single reaction within a sample as standard PCR, however, the sample is separated into a large number of partitions, and the reaction is carried out in each partition individually.
What is droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) and how does it work?
Droplet digital PCR relies on the partitioning of the tested sample into thousands of single samples thanks to the generation of droplets. For performing the assay, the sample volume is split in such a way that each droplet contains either one or none of the target DNA molecules. The droplets act as laboratory wells, each containing a sample, and being able to host a PCR reaction in within. Due to the small droplet volume, the PCR reaction runs very efficiently even from a single molecule. During amplification, a fluorescent dye is formed or activated. The positive droplets become fluorescent. Absolute quantitation of the number of target molecules is simplified to the count of fluorescence active droplets in the generated droplet collection. ddPCR is an excellent example of a transition of a microfluidic system from the academic field to industry.
What are the advantages of ddPCR?
The major advantage of droplet digital PCR is the possibility to perform absolute quantitation of the number of target molecules, which is simplified to the count of fluorescence active droplets in the generated droplet partition. The separation allows for more reliable collection and sensitive measurement of nucleic acid amounts. Precision is drastically enhanced [1], and no standard curves or calibration standards are necessary to assess the quantity of the sample of interest. The separation in multiple droplets containing nanoliters of reagent drastically reduces the time and reagents needed to perform a classical PCR reaction. This allows to reduce consumable and reagent costs, which makes it a one-of-a-kind cost effective method.
Main applications using droplet digital PCR technology
Liquid biopsy
Liquid biopsies are non-invasive tests performed on blood samples to detect cancer cells circulating in the blood (circulating tumor cells, CTCs) or pieces of DNA from tumor cells in the blood. This technique is increasingly used for cancer detection and monitoring, as it is low risk for the patient and helps doctors understand what kind of molecular changes are taking place in the tumor. Droplet Digital PCR (ddPC) provides the level of sensitivity required for liquid biopsy.
Copy number variation
A key measurement challenge in diagnostic research involves identifying small changes in nucleic acid sequence that are commonly associated with genetic diseases. Changes in the genomic DNA leading to an abnormal copy of a DNA sequence are called copy number variations (CNVs). They are present in complex diseases such as Down’s Syndrome and many cancers.
Pathogen Detection and Microbiome Analysis
Droplet digital PCR is extensively used in microbiology.. Digital PCR’s ability to amplify low concentration targets in complex backgrounds and show higher sensitivity than standard PCR makes it the technology choice for microbiome analysis.
Resources
-
Microfluidics case studies OEM Case Study: Microfluidic Drug Screening Read more
-
Expert Reviews: Basics of Microfluidics Microfluidics for vaccine development Read more
-
Microfluidic Application Notes High-throughput cell DNA screening using digital PCR Read more
-
Microfluidic Application Notes Analysis of a commercial surfactant for digital PCR assay Read more
-
Expert Reviews: Basics of Microfluidics Microfluidic Droplet Production Method Read more
-
Expert Reviews: Basics of Microfluidics Flow control for droplet generation using syringe pumps and pressure-based flow controllers Read more
Importance of fluid handling for droplet digital PCR applications
Droplet digital PCR relies on random distribution of dPCR mix containing target molecules on the partition of equivalent volumes (here, the droplets). In this way, some partitions contain no target molecules, while the remaining partitions contain at least one molecule. Partitions are next categorized and counted as positive or negative depending on their fluorescence intensity. The calculations are derived from a Poisson model, which can be impacted by partition volume since the model assumes the partition to be monodisperse. As a consequence, a heterogeneous droplet population can affect the droplet digital PCR process. In fact, several groups demonstrated through different studies that partition droplet volume variability can cause a bias on the accuracy of the measurements.
More information can be found in the paper written by Emslie et al.: Droplet Volume Variability and Impact on Digital PCR Copy Number Concentration Measurements The impact of flow rate on droplet size using a microfluidic system is today well described in the literature. Thus, to avoid heterogeneous droplet populations that can affect the droplet digital PCR process, one should consider using a precise flow controller.
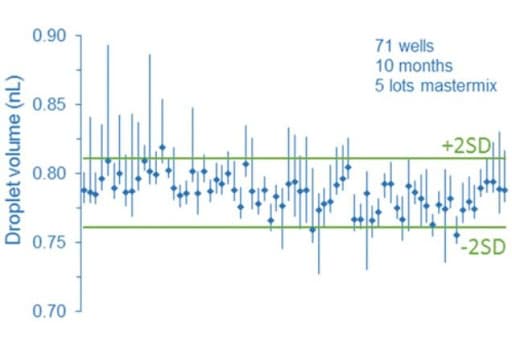
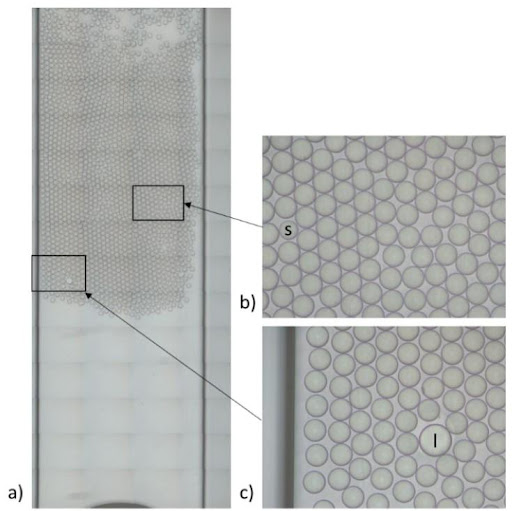
Flow control systems for industrial digital PCR
Flow rate stability is thus critical for having repeatable reactor volumes and reproducible results in droplet digital PCR experiments. Syringe pumps are commonly used for generating droplets. Depending on the model in use, syringe pumps show limited flow control. As a consequence, the droplet size, proportional to the flow rate, is affected. In addition, the actual flow rate cannot be monitored with such devices. The flow rate value is displayed on the device, but no information on the time required for reaching a set flow rate is given (the time for flow equilibrium may vary depending on the microfluidic setup, and flow can oscillate depending on the instrument). An alternative to syringe pumps is pressure-based flow controllers. These show that high-precision flow control, fast reaction time, and flow monitoring are possible.
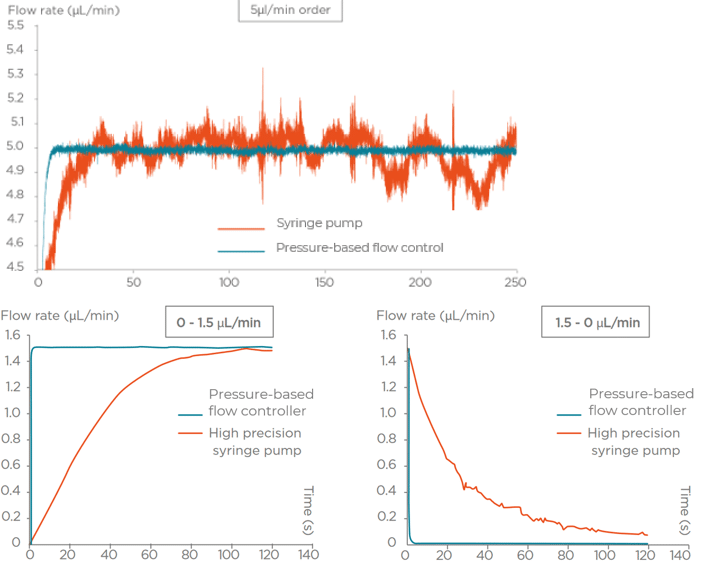
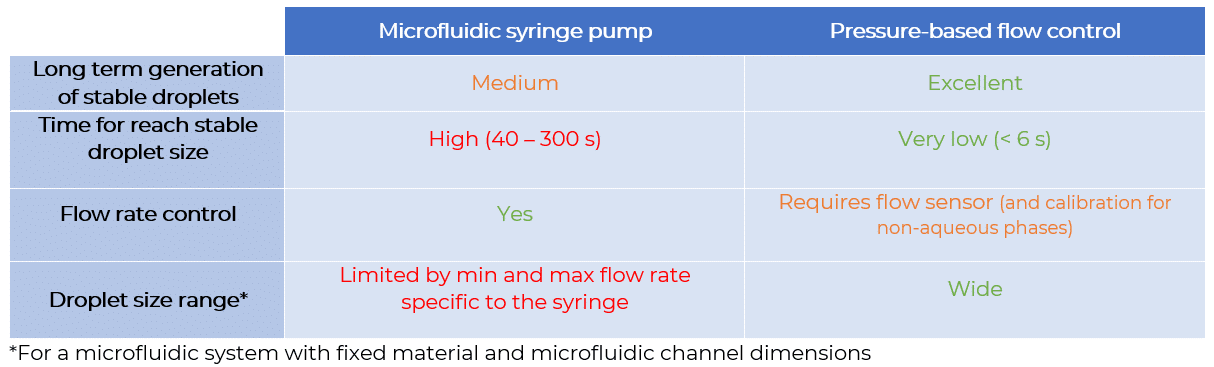
We compared the production of water-in-oil emulsions using microfluidic syringe pumps and pressure-based flow controllers. Using pressure control, the desired droplet size is quickly obtained (< 6 s), and monodisperse droplet generation is ensured over time. Thus pressure controllers are the instruments of choice for droplet digital PCR.
The benefits of choosing Fluigent for your ddPCR system
- Best in class stability: < 0.5% due to our field-proven, patented FASTAB™ technology allowing optimal flow control with the robustness required in demanding industrial environments.
- Straightforward workflow automation included in Fluigent’s software
- An expert engineering time specializing in microfluidic design and mechanical and software integration
References
1. Whale, A. S. et al. Comparison of microfluidic digital PCR and conventional quantitative PCR for measuring copy number variation. Nucleic Acids Research40, (2012).
2. Emslie, K. R. et al. Droplet volume variability and impact on digital pcr copy number concentration measurements. Analytical Chemistry91, 4124–4131 (2019).
3. Emslie, K. R. et al. Supporting information Droplet volume variability and impact on digital PCR copy number concentration measurements Author names and affiliations.